Intel Shifts to Foundry Business, Aims for No. 2 Spot by 2030
Insights | 17-05-2024 | By Robin Mitchell
Intel's recent announcement to become the world's second-largest foundry by 2030 marks a significant shift in focus compared to its decision to exit the ASIC design services business 20 years ago. Back then, Intel's move to discontinue its ASIC services unit raised questions about its alignment with core strategies. As the company redirected its ASIC design resources internally, it left behind speculation about margins and market trends. The decision not to offer EDA tools or fab processes to its ASIC customers added another layer of complexity to the situation. What challenges has Intel faced over the past decade, what strategies is Intel employing to achieve its goal of becoming the world's second-largest foundry, and how might the landscape of the semiconductor industry evolve with Intel's renewed focus on foundry services?
- Intel has faced challenges in margins, market trends, and resource allocation in its ASIC design services, impacting its financial performance and relationships with customers.
- Intel's strategic shift towards becoming a major player in the foundry market highlights its commitment to growth and customer-centric innovation.
- Intel's focus on foundry services will reshape the semiconductor industry landscape, drive innovation, enhance supply chain resilience, and influence global technological advancements.
Navigating the Challenges: Intel's Journey Over the Past Decade
Semiconductor technology has a rich historical context, with Intel playing a pivotal role in shaping the industry. Intel's contributions to the development of microprocessors have been crucial in changing computing. However, despite its historical significance, Intel has encountered numerous challenges over the past decade that have tested its position in the market.
One of the key challenges that Intel has dealt with is the issue of margins and market trends, particularly in the ASIC design services business. As semiconductor technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the pressure to maintain competitive pricing while ensuring profitability has intensified. Intel's struggle to navigate these market dynamics has put a strain on its financial performance and market share.
Additionally, Intel's decision not to offer EDA tools or fab processes to its ASIC customers has added another layer of complexity to its challenges. By limiting the tools and processes available to its customers, Intel has created a barrier that hinders the full potential of its ASIC design services. This decision has not only impacted the competitiveness of Intel's offerings but has also alienated customers who seek comprehensive solutions from their semiconductor partners.
Intel has also suffered from its CPU business numerous times in the past due to the closely coupled link between its CPU technologies and process nodes. While this coupling does allow Intel to take full advantage of their process nodes, it also means that any delay in getting the node ready also delays the release of new devices. For the vast majority of Intel's history, this has never been an issue, but the development of nanometer scales has seen multiple nodes missed, including the recent 7nm and 5nm technologies.
Finally, as technologies such as RISC-V continue to rise, Intel is faced with an increasingly uphill battle. Such open-source processors could provide designers with far cheaper options that focus on energy consumption over computational performance, something that is critical in modern embedded devices.
Intel's Strategies for Becoming the World's Second-Largest Foundry
Intel, a leader in the semiconductor industry, has recently announced a major shift aimed at reshaping its market position. The tech giant is targeting to become the world's second-largest foundry by the year 2030. This strategic shift signifies a major change in Intel's business direction, highlighting its dedication to growing its foundry market presence.
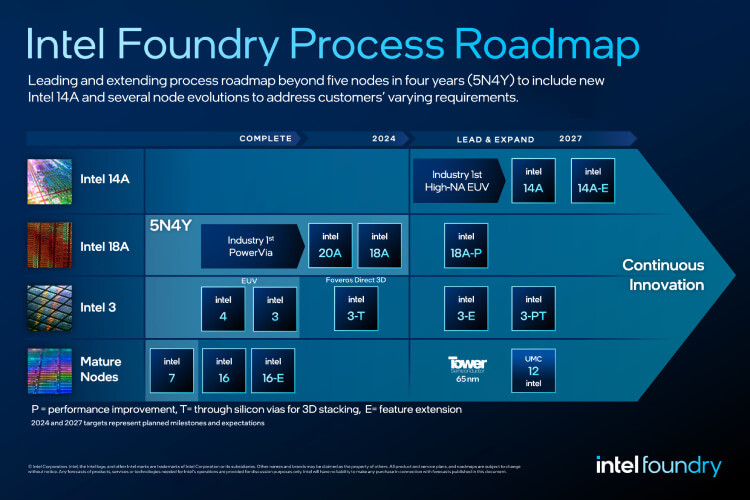
Announced at the Intel Foundry Direct Connect event, Intel's roadmap includes the introduction of Intel 14A process technology and several specialised node evolutions. These advancements are designed to meet the demands of AI and other cutting-edge applications, reinforcing Intel's commitment to leading the semiconductor industry in innovation and technology.
This renewed emphasis on foundry services is a notable change from Intel's decision two decades ago to leave the foundry sector. In January 2003, Intel chose to stop its Asic design services business, stating it didn't align with its main strategies. Despite this, Intel continued to use its resources and talent for internal projects, indicating a move away from external ASIC vendors.
Support from Ecosystem Partners
During the event, Intel also highlighted significant support from ecosystem partners such as Synopsys, Cadence, Siemens, and Ansys. These partners are essential in providing validated tools, design flows, and IP portfolios that will enable Intel Foundry customers to accelerate their advanced chip designs, particularly for AI applications.
To reach its goal of becoming a key player in the foundry market, Intel has launched several strategic initiatives. By maintaining strong connections with current customers and ensuring the completion of ongoing products in the Asic services pipeline, Intel is facilitating a smooth shift to a foundry-focused model. Additionally, Intel is reallocating resources, moving its ASIC design resources internally to optimise operations and advance semiconductor design.
Intel's ambitious "five-nodes-in-four-years" process roadmap, which includes Intel 18A, is central to its strategy. This roadmap aims to deliver the industry's first backside power solution, a significant advancement that enhances power delivery and efficiency in advanced node designs. This innovation is expected to set new standards in the semiconductor industry.
Customer-Centric Approach and Strategic Partnerships
Maintaining solid relationships with existing customers is central to Intel's strategy for expanding its foundry services. By working closely with customers and meeting their needs during this change, Intel aims to maintain its status as a reliable partner in the semiconductor sector. This focus on customer needs highlights Intel's commitment to providing top-notch foundry services and ensuring an efficient transition for its clients.
Moreover, Intel's collaboration with leading technology companies was underscored by Microsoft's announcement of choosing a chip design for production on the Intel 18A process. This partnership exemplifies the confidence major industry players have in Intel's advanced process technologies and its ability to deliver high-performance, reliable semiconductor solutions.
With its goal to become the world's second-largest foundry by 2030, Intel's strategic emphasis on foundry services is a key development in its growth. By drawing on its semiconductor technology expertise and adopting a customer-focused strategy, Intel is poised to meet the increasing demand for advanced chip manufacturing solutions. As the semiconductor industry evolves, Intel's ambitious vision for its foundry services reflects its dedication to leading-edge technology, excellence, and sustained industry growth.
The Evolution of the Semiconductor Industry with Intel's Foundry Services Focus
Intel's renewed focus on foundry services is set to significantly impact the competitive landscape within the semiconductor industry. By aiming to become the world's second-largest foundry by 2030, Intel is poised to challenge existing players like TSMC and Samsung. This move will not only create healthy competition but also drive innovation and technological advancements across the industry. With Intel's strong reputation and expertise in semiconductor technology, the company's entry into the foundry market will undoubtedly shake up the competitive dynamics, pushing other players to elevate their offerings and services to stay ahead in the game.
The expansion of Intel's foundry services also opens up exciting opportunities for innovation and collaboration within the semiconductor sector. As Intel reallocates its resources and focuses on optimising operations, there is a potential for increased collaboration with other industry players, startups, and research institutions. This collaborative approach can foster the development of cutting-edge technologies, new chip designs, and novel solutions that can significantly impact the semiconductor landscape. By leveraging Intel's expertise and resources, engineers and innovators can explore new possibilities and drive forward the next wave of technological advancements in the industry.
Opportunities for Innovation and Collaboration
Intel's growth in the foundry market will have significant implications for the overall supply chain resilience in the semiconductor industry. By expanding its foundry services, Intel can contribute to diversifying the supply chain and reducing dependency on a few key players. This diversification can enhance the industry's resilience to disruptions, such as those experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic or geopolitical tensions. Intel's presence in the foundry market can offer alternative options for semiconductor manufacturing, ensuring a more robust and flexible supply chain that can adapt to changing market dynamics and challenges.
The strategic shift of Intel towards becoming a leading foundry will also have a significant impact on the global technological ecosystem and future developments in electronics engineering. Intel's strong commitment to advancing semiconductor technology and providing top-notch foundry services can drive innovation across various industries, from consumer electronics to automotive and healthcare. The company's expertise and resources can catalyze the development of advanced technologies, such as AI, IoT, and 5G, shaping the future of the global technological landscape.
Finally, Intel's renewed focus on foundry services is poised to bring about a wave of positive changes in the semiconductor industry. From reshaping the competitive landscape and fostering innovation to enhancing supply chain resilience and influencing the global technological ecosystem, Intel's strategic shift holds immense potential for driving growth and advancement in the field of electronics engineering. Engineers and industry stakeholders can look forward to a future filled with opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and technological breakthroughs as Intel paves the way for a new era in the semiconductor industry.

